Tides are a fascinating natural phenomenon that greatly influence Earth’s oceans. The scientific explanation of tides lies in the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun on the Earth, which causes the sea levels to rise and fall cyclically. This movement creates high and low tides, which happen at regular intervals along coastlines around the world.
As the Earth rotates, different areas pass through the tidal bulges created by these gravitational forces. The Moon, being the closest celestial body to Earth, has the strongest effect on tides.
However, the gravitational pull of the Sun also plays a significant role, particularly during full and new moons when high tides are at their highest.
Understanding tides is essential not just for marine activities, but also for ecology, navigation, and even coastal management.
This article will explore the mechanics behind tides, how they affect the environment, and their significance in our daily lives.
Mechanics of Tidal Forces
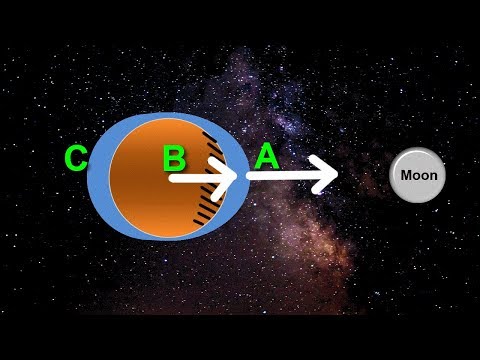
Tidal forces result from gravitational interactions between the Earth and other celestial bodies, chiefly the Moon and the Sun. Understanding these forces involves looking at how gravity affects water movement and how Earth’s movement contributes to tides.
Gravitational Pull and the Tidal Cycle
The gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun creates a tractive force on Earth’s waters. This pull leads to the formation of tidal bulges—areas where water rises higher due to gravitational attraction.
As Earth rotates, these bulges move, causing the tides to change every six hours on average. The tidal cycle typically includes two high tides and two low tides each day.
The strength of the tidal force varies with the distance of the Moon and Sun. When they are closer, the gravitational pull is stronger, resulting in a greater tidal range.
The Influence of the Moon and Sun
The Moon has a more significant effect on tides than the Sun because it is much closer to Earth. Its gravitational attraction causes the primary tidal bulges.
While the Sun’s gravitational pull is less intense, it is still important.
When the Sun, Moon, and Earth align during full and new moons, the combined gravitational forces create spring tides that lead to higher high tides and lower low tides.
Conversely, during the first and third quarters of the Moon, the Sun and Moon are at right angles. This arrangement leads to neap tides, which have a smaller tidal range.
Interaction of Earth’s Rotation and Tides
Earth’s rotation plays a crucial role in the timing of tides. As the planet spins on its axis, the tidal bulges shift position, affecting when and where tides occur.
On average, the earth tide takes about 12 hours and 25 minutes to complete one full cycle, which is slightly longer than a typical day. This difference is due to the Moon’s orbit around Earth.
The interaction between Earth’s gravity and the tidal forces means that as Earth rotates, some areas experience high tide more than others. This creates a complex pattern of water movement that varies with geography and local conditions.
Types and Effects of Tides

Tides create regular patterns in sea levels, affecting coastlines and the environment. Different types of tides have unique characteristics and play significant roles in marine ecosystems and human activities. The following sections will explore these variations, their functions, and their extremes.
Variations of Tides and Their Occurrence
Tides can be categorized into high and low tides, which occur due to the gravitational pull of the moon and sun. In general, high tides happen twice a day, while low tides fall in between.
The Bay of Fundy is famous for having some of the highest tidal ranges in the world. Tidal heights here can reach over 50 feet. Such significant differences happen because of the unique shape of the coastline and the bay’s depth.
Tidal currents also vary with the phases of the moon. During spring tides, which occur during full and new moons, tidal amplitudes are at their highest. Conversely, neap tides, occurring during the first and third quarters of the moon, have lower tidal heights. This combination of factors affects how ocean waters move along the coast and impact marine habitats.
Influence on Marine Life and Human Activities
Tides greatly influence marine ecosystems, dictating the timing of feeding and breeding for various species. Many organisms, such as crabs and shorebirds, rely on the shifting tides to access food sources along the coastlines.
Tides also affect human activities, particularly in coastal waters. Fishing schedules and boat navigation depend heavily on tidal patterns. Understanding tidal currents can help fishermen locate schools of fish effectively.
Additionally, tides can influence water quality in estuaries. As high tide floods into landmasses, it brings nutrients that support plant and animal life, promoting biodiversity. Low tides expose sections of coast, allowing organisms to thrive in tidal pools and intertidal zones.
Extremes of Tides: From Neap to Spring Tides
Tides are not always consistent. They vary between spring and neap tides, resulting in extremes that significantly affect coastal environments.
Spring tides cause substantial changes in sea level, often leading to flooding in low-lying areas. Meanwhile, neap tides, with their smaller tidal heights, can have a calming effect on coastal waters.
The difference in tidal ranges can also create amphidromic points, where water moves in a circular pattern rather than rising or falling. Understanding these extremes is crucial for coastal planning and management.
For instance, areas prone to high tides require careful monitoring to prevent flooding. The dynamics of tidal heights shape entire ecosystems and human infrastructure along coastlines.

